

EFFICACY
PAXLOVID was evaluated in the EPIC-HR pivotal trial1
On this page:

This trial included a geographically diverse group of 2113 participants1,2
Trial design1,2
EPIC-HR was a phase 2/3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in nonhospitalized, symptomatic adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection with ≥1 risk factor for progression to severe disease (N=2113).


Primary efficacy endpoint


The primary efficacy endpoint analysis was conducted in the mITT, mITT1, and mITT2 analysis sets.
- mITT (modified intent-to-treat) analysis set=all treated participants with onset of symptoms within 3 days who at baseline did not receive nor were expected to receive COVID-19 therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment1
- mITT1 analysis set=all treated participants with onset of symptoms within 5 days who at baseline did not receive nor were expected to receive COVID-19 therapeutic mAb treatment1
- mITT2 analysis set=all treated participants with onset of symptoms within 5 days1

Participant inclusion criteria1
- Unvaccinated
- ≥18 years of age
- Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection
- COVID-19 symptom onset within 5 days
EPIC-HR was initiated on July 16, 2021, during early vaccination efforts; therefore, PAXLOVID was studied in the absence of vaccine-induced immunity.3

Select exclusion criteria1
- Individuals with a history of prior COVID-19 infection or vaccination
- Individuals taking any medications with clinically significant drug interactions with PAXLOVID

Eligible participants also had ≥1 of the following risk factors for progression to severe COVID-191:













‡According to the latest CDC guidance, hypertension is a mixed-evidence high-risk factor.4
Based on the latest guidance, some of these high-risk inclusion criteria differ from the CDC’s list of high-risk factors (eg, the CDC defines high risk as age 50+).4 PAXLOVID is indicated for use in patients at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.1§
§This link will take you to a website that is owned and operated by the CDC. Pfizer is not responsible for the content or services of this site.

mITT analysis sets1,2
2113 participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either PAXLOVID or placebo
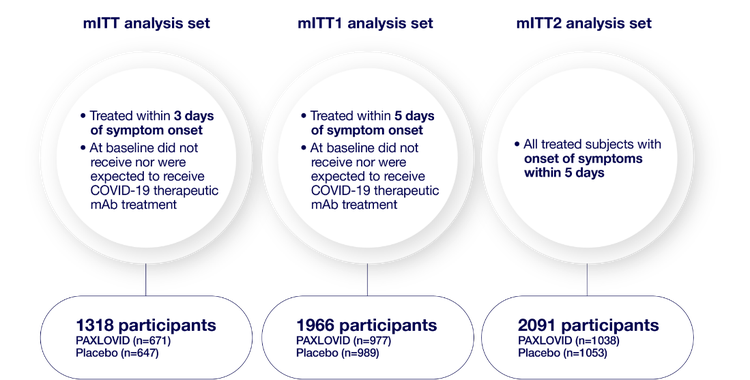

Consistent primary efficacy endpoint results were observed across each analysis set: mITT, mITT1, and mITT2.1

Participant demographics1,2
PAXLOVID was studied in a population identified from sites around the world.
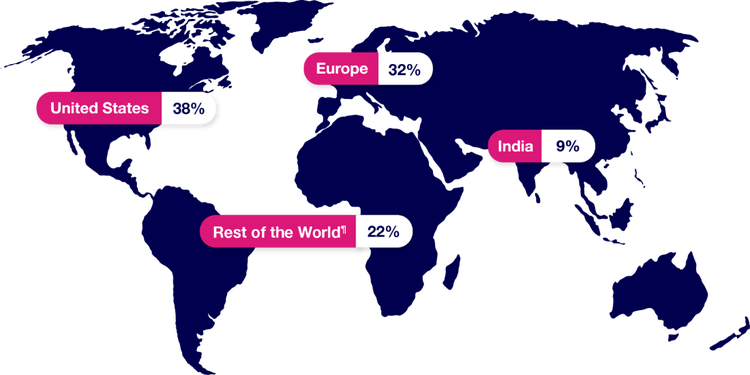
¶“Rest of the World” consists of Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Peru, Russian Federation, South Africa, Republic of Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, and Turkey.
Sex
- 51% were male
- 49% were female
Mean age
- 45 years, with 20.7% of participants ≥60 and 79.3% of participants <60

Most frequent high-risk factors in EPIC-HR participants1,2
At baseline, the most common underlying medical conditions and factors associated with high risk of progression to severe COVID-19 included in EPIC-HR were:
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were balanced between the PAXLOVID and placebo groups.
- 1263 participants (59.8%) had 2 or more such characteristics or coexisting conditions
#According to the latest CDC guidance, hypertension is a mixed-evidence high-risk factor.4

Trial limitations
- PAXLOVID was approved based primarily on the EPIC-HR trial, a single randomized clinical trial that has not been replicated1
- No vaccinated patients were included in the trial; however, 49.1% of participants were SARS-CoV-2 seropositive at baseline1,2
- The CDC high-risk criteria differ in some aspects from the EPIC-HR trial risk factor inclusion criteria1,4
What would you like to learn more about?
Drug Interactions
View boxed warning, contraindicated drugs, and other potentially significant drug interactions.
Dosing
Learn about the standard, reduced, and severe renal impairment doses of PAXLOVID.
Safety
Find out about the safety data from clinical studies and post-authorization experience and how to report an adverse event.
BMI=body mass index; CDC=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; CI=confidence interval; COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019; mAb=monoclonal antibody; mITT=modified intent-to-treat; SARS-CoV-2=severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
References:
- Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for PAXLOVID®. Pfizer Inc.; 2025.
- Data on File. CSR. Pfizer Inc.; 2023.
- Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397-1408.
- Underlying conditions and the higher risk for severe COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated February 6, 2025. Accessed February 12, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/hcp/clinical-care/underlying-conditions.html