
How PAXLOVID works
What happens when SARS-CoV-2 enters the body?
When SARS-CoV-2 enters the host cell, viral RNA translation leads to the formation of 2 large polyproteins, pp1a and pp1ab.1,2
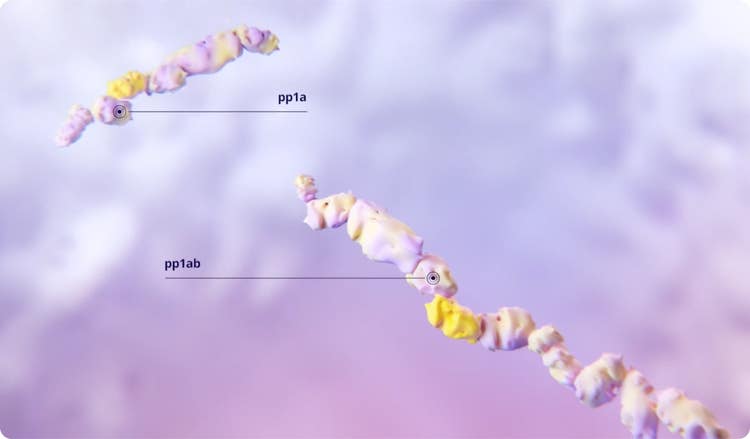
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) cleaves the polyproteins’ chains to release the individual functional proteins that are critical for viral replication.1-4

What is the mechanism of action of PAXLOVID?
PAXLOVID consists of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. Nirmatrelvir is a peptidomimetic inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro renders it incapable of processing the viral polyproteins pp1a and pp1ab, preventing viral replication.5
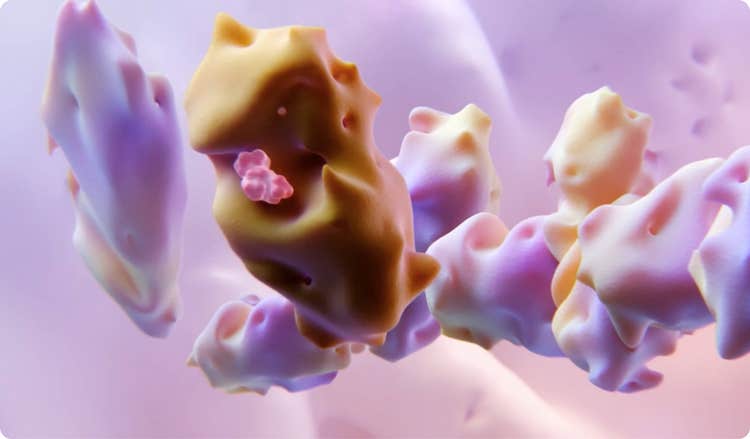
Ritonavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor, but is not active against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. Ritonavir inhibits the CYP3A-mediated metabolism of nirmatrelvir, resulting in increased plasma concentrations of nirmatrelvir.5
What would you like to learn more about?
Drug Interactions
View boxed warning, contraindicated drugs, and other potentially significant drug interactions.
Dosing
Learn about the standard, reduced, and severe renal impairment doses of PAXLOVID.
Safety
Find out about the safety data from clinical studies and post-authorization experience and how to report an adverse event.
COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019; HIV=human immunodeficiency virus; Mpro=main protease; RNA=ribonucleic acid; SARS-CoV-2=severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
References:
- Eastman RT, Roth JS, Brimacombe KR, et al. Remdesivir: a review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19. ACS Cent Sci. 2020;6(5):672-683.
- Pluskota-Karwatka D, Hoffmann M, Barciszewski J. Reducing SARS-CoV-2 pathological protein activity with small molecules. J Pharm Anal. 2021;11(4):383-397.
- Owen DR, Allerton CMN, Anderson AS, et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021;374(6575):1586-1593.
- Senger MR, Evangelista TCS, Dantas RF, et al. COVID-19: molecular targets, drug repurposing and new avenues for drug discovery. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2020;115:e200254.
- Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for PAXLOVID™. Pfizer Inc.; 2025.

